Design and Analysis of a Savonius Wind Turbine
Savonius wind turbines are drag-based machines. As air flows over the blades, the drag force components on one side of the turbine are higher than on the opposite side, producing a torque. As the turbine rotates, this torque fluctuates, but remains positive. Savonius turbines do not require an external power source to start turning, and thus are very convenient for small to medium-sized power generators, for example on buildings and boats. They are also mechanically simple and typically easy to design for high wind speeds, for example when used in remote or high altitude locations.
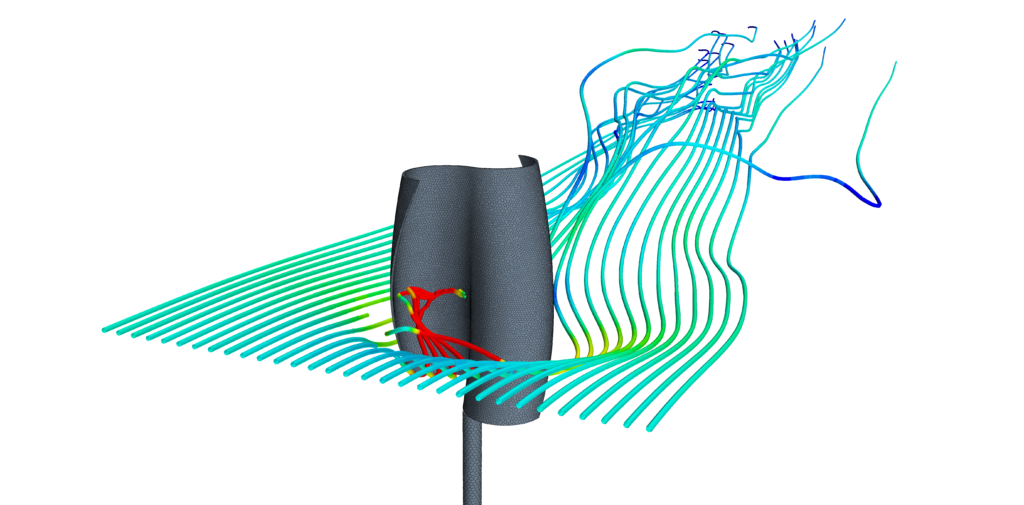
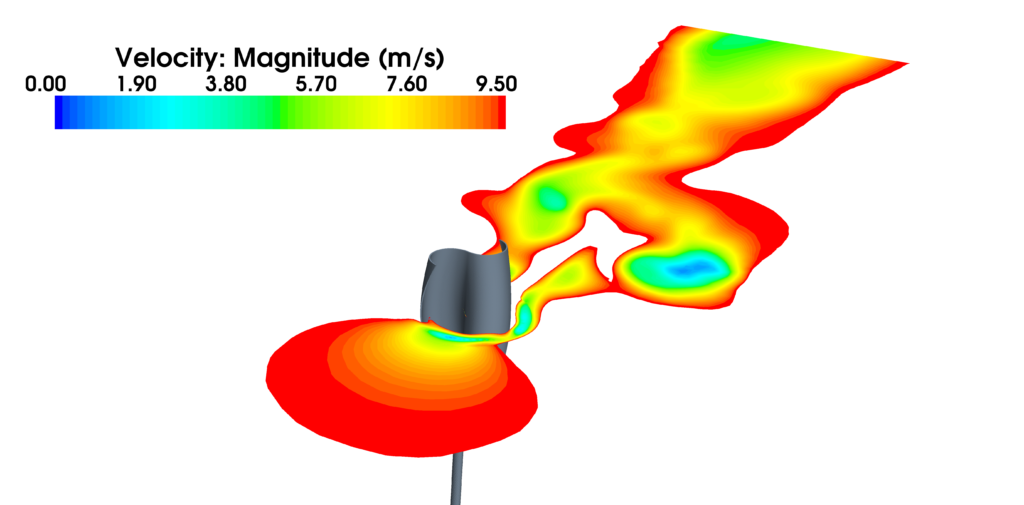
Shown below is a Kumair vertical axis (VAWT) savonius wind turbine design. CFD analyses provided air loads, allowing optimization of the power generation. Click the pictures to see larger images. The image on the left shows streamlines, while on the right velocity magnitude contours are plotted on a plane perpendicular to the axis of the rotation.
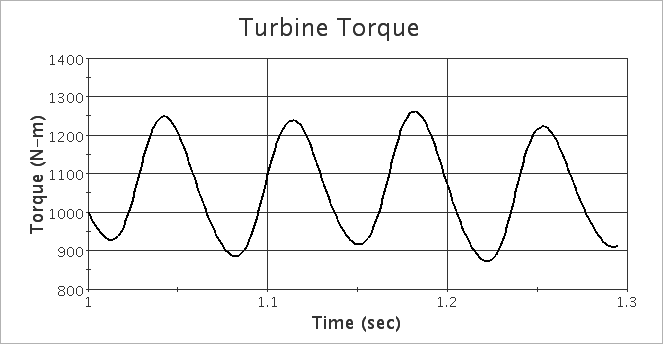
CAD modeling was done in Solidworks and CFD analyses in Star-CCM+. For the case shown, the calculation is 3D unsteady with a rotating mesh. The mean torque is approximately 1,100 N-m, and was calculated by outputting the total moment about the rotation axis each time step, and then averaging over several full periods.
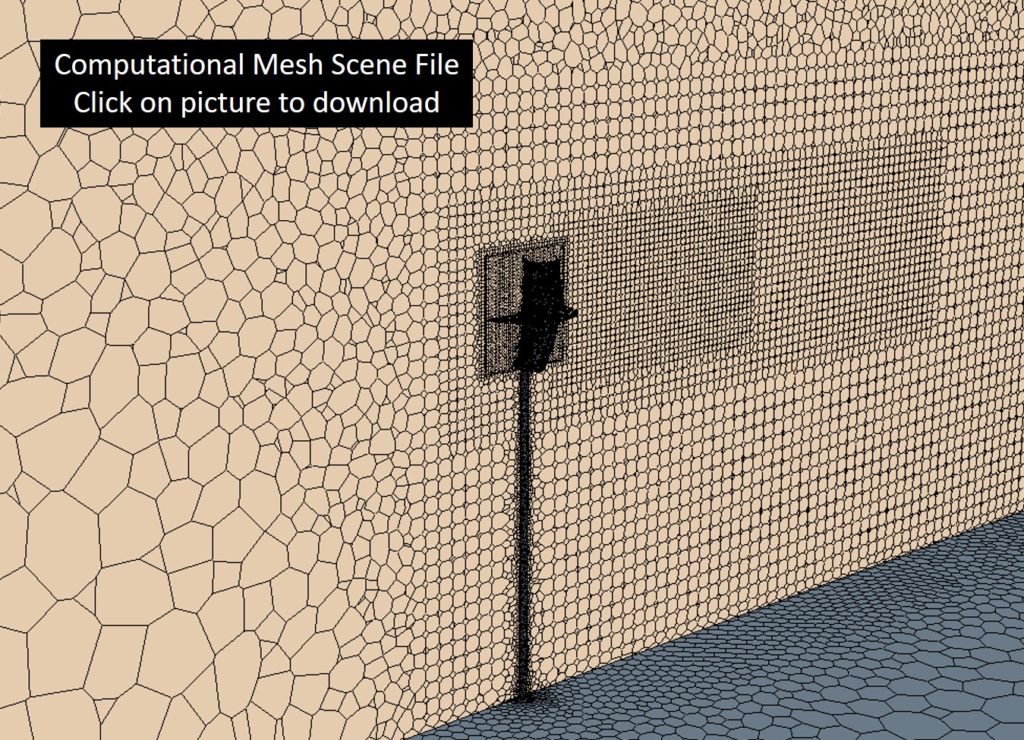
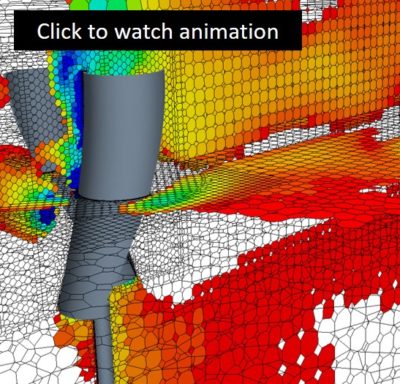
Computational Modeling Scene Files
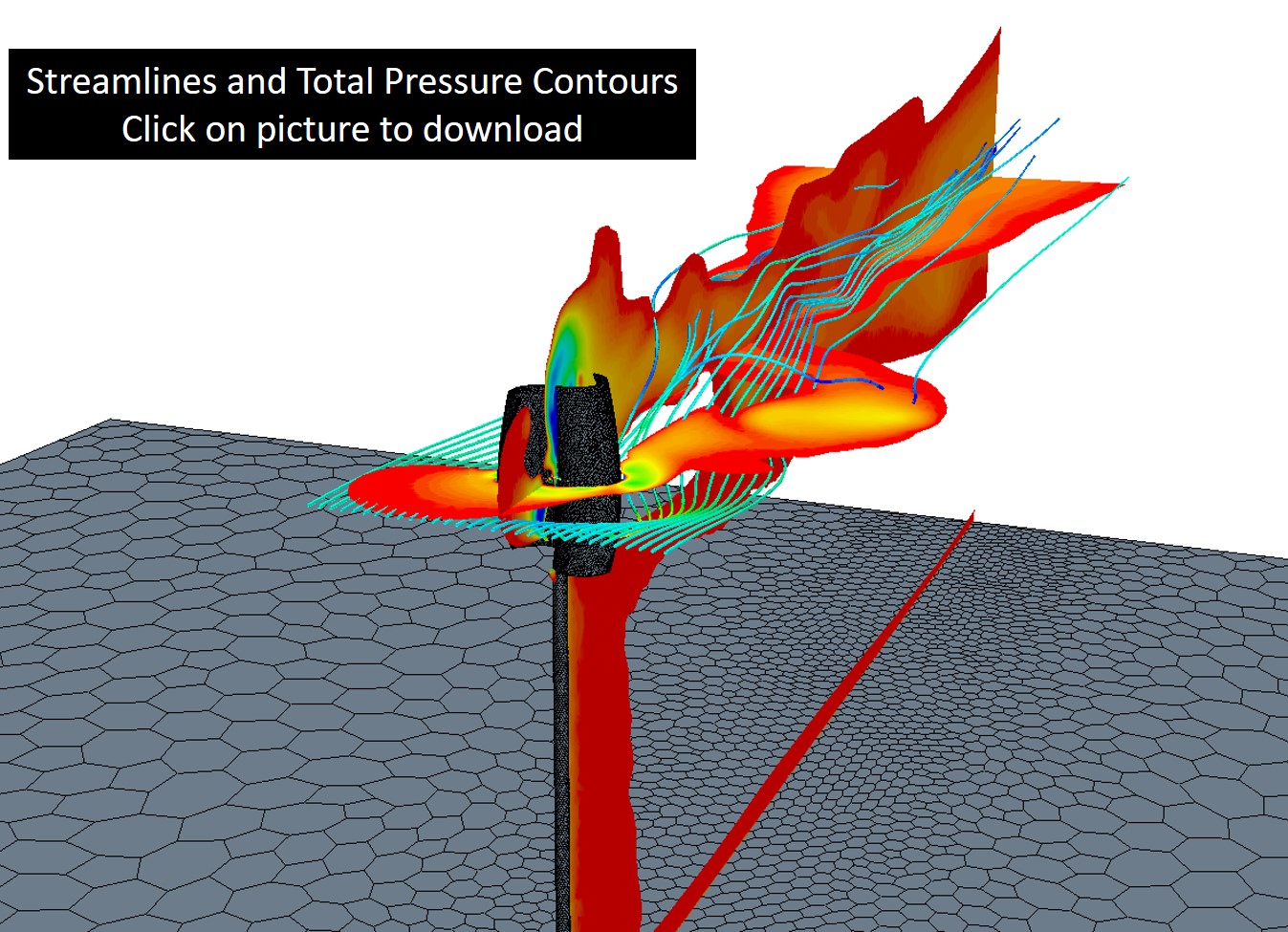
Click the pictures below to download two Star-CCM+ scene files. The first details the computational mesh used to perform the unsteady CFD calculations. The second shows streamlines and total pressure contours on two mid-planes cutting through the wind turbine.
To learn more about Kumair's design and analysis capabilities read our other technical pages, or email us through our contact page. Kumair offers no cost, no obligation evaluation of your project, as well as ROMs and quotes for both new and existing customers.