How to Take a Screenshot on Ubuntu
Want to take a screenshot on Ubuntu? You can do so easily using the steps in this guide.
Screenshots are a really useful way to take a clean snapshot of what you’re currently doing on your PC. I use them in articles like this one, showing exactly where (and how) to perform the actions needed to fix a problem or perform a task. On Ubuntu, you can take a screenshot in a few different ways, depending on the app you’re using. You can capture the whole screen or only capture a small section. I’ll explain all the different ways you can take screenshots on Ubuntu.
How to Take a Screenshot on Ubuntu
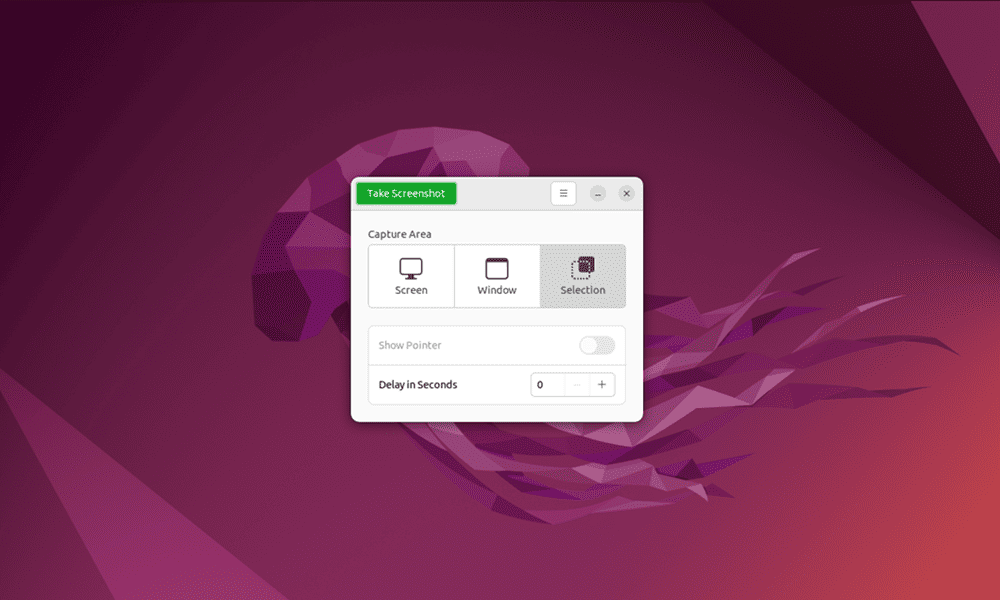
The best way to take screenshots on Ubuntu is to use the Print Screen (or PrntScrn) key on your keyboard. Pressing this key will bring up options to capture the whole screen, the current window, or a custom selection using your mouse.
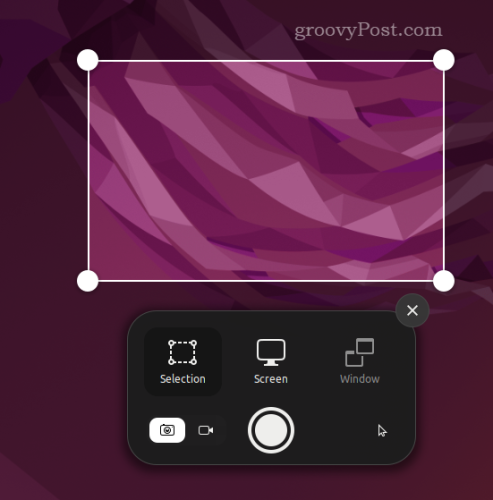

Screenshots will appear in your Pictures folder, typically named with the date and time in the filename.
There are also keyboard shortcuts you can use to take screenshots automatically. These include Alt+Print to grab a screenshot for the currently active window and Shift+Print Screen to grab a screenshot for the entire screen.
How to Install and Use the GNOME Screenshot Tool in Ubuntu
GNOME Screenshot was the default screenshot tool in earlier Ubuntu releases. It’s been replaced in more recent releases, but if you prefer to use it, you can install it again using the terminal. To install the GNOME Screenshot tool, follow these steps.
- Open your terminal by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T.
- In the terminal, type sudo apt install gnome-screenshot.

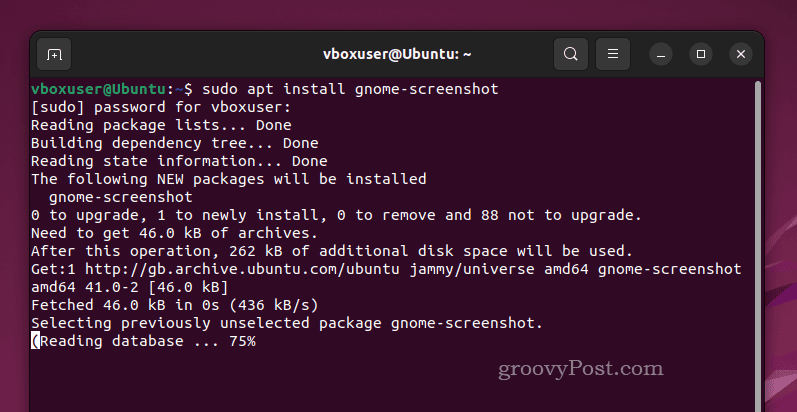
- Enter your password when prompted and wait for the process to complete.
- Once installed, using GNOME Screenshot is straightforward. To launch the tool, open your applications menu and select Screenshot.

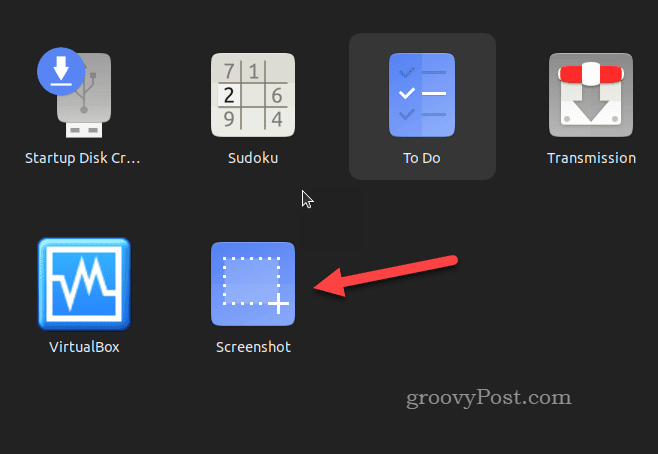
- Once GNOME Screenshot is running, you can use the on-screen GUI to take screenshots.

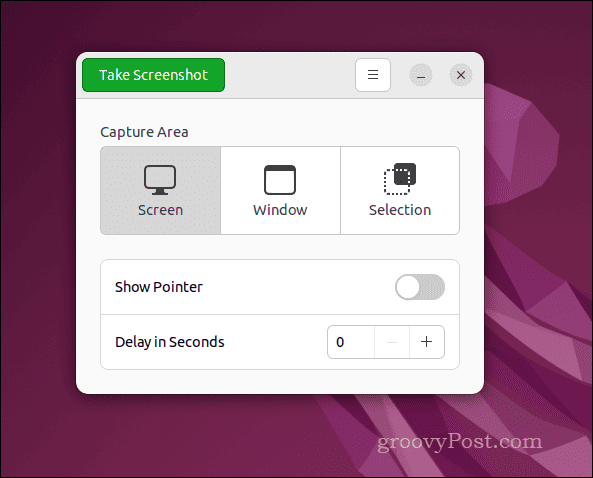
- Alternatively, you can use keyboard shortcuts to take screenshots on your Ubuntu PC. Press Print Screen for your entire screen, Alt+Print Screen to capture the current window, or use Shift+Print Screen to select an area manually.
How to Take Ubuntu Screenshots Using the Terminal
In Ubuntu, you can also capture screenshots directly from the terminal. Most users will probably prefer to use other methods, but you may still want to use terminal commands to document the output of your terminal session or if you’re using Ubuntu server without a GUI, for instance.
The best way to do this is to use GNOME Screenshot, the previously used tool as the default screenshotting tool in Ubuntu.
- First, open a new terminal window. If you’ve not installed GNOME screenshot already, type sudo apt install gnome-screenshot and press Enter.
- Insert your password, if prompted, to complete the installation.


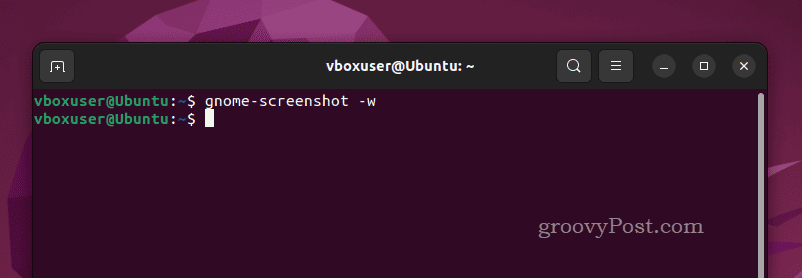
- Once installed, type gnome-screenshot -w to take a screenshot of the current terminal window and press Enter.

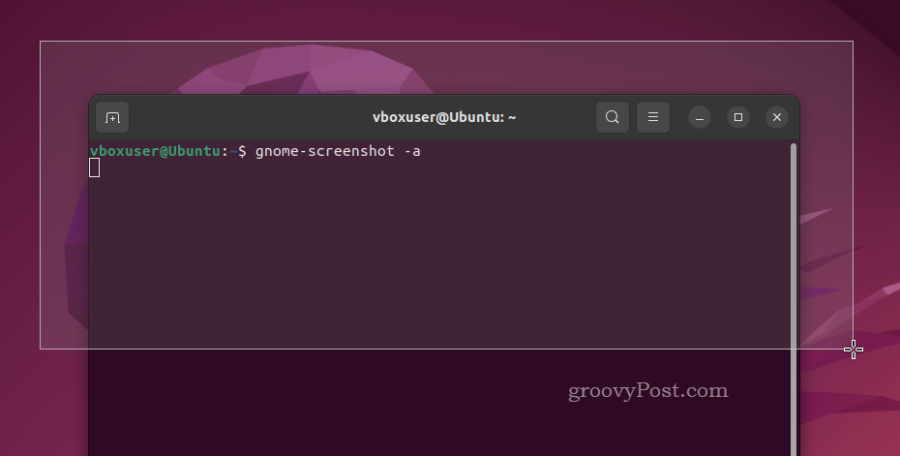
- To grab a screenshot of an area of the screen, type gnome-screenshot -a and press Enter. Use your mouse to drag and select an area of the screen—the image will immediately be saved after you select the area.

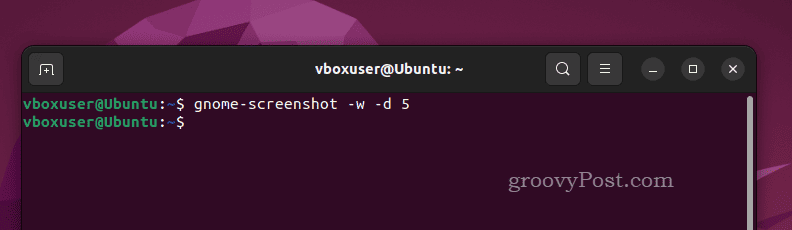
- If you want to include a delay, allowing you time to select a new window or rearrange your screen, type gnome-screenshot -d 0, replacing 0 with the desired number of seconds. You can also mix this with other flags, such as gnome-screenshot -w -d 5 to take a screenshot of the active window after five seconds.

As with other methods, screenshots will save automatically into your Pictures folder.
Taking Screenshots on Ubuntu
No matter what app you decide to use you take a screenshot on Ubuntu, the process should be fairly straightforward. Most apps will take advantage of the built-in Print Screen button on your keyboard, but you can also use keyboard shortcuts and on-screen GUI apps to help you do it (as well as terminal commands).
If you run into any issues, don’t be afraid to give another app a try. Ubuntu’s built-in screenshot tools are good enough, but a tool like Flameshot will allow you to edit your screenshots, too.
